吴裕雄--天生自然 PYTHON数据分析:威斯康星乳腺癌(诊断)数据分析(续一)
drop_list1 = ['perimeter_mean','radius_mean','compactness_mean','concave points_mean','radius_se','perimeter_se','radius_worst','perimeter_worst','compactness_worst','concave points_worst','compactness_se','concave points_se','texture_worst','area_worst']
x_1 = x.drop(drop_list1,axis = 1 ) # do not modify x, we will use it later
x_1.head()
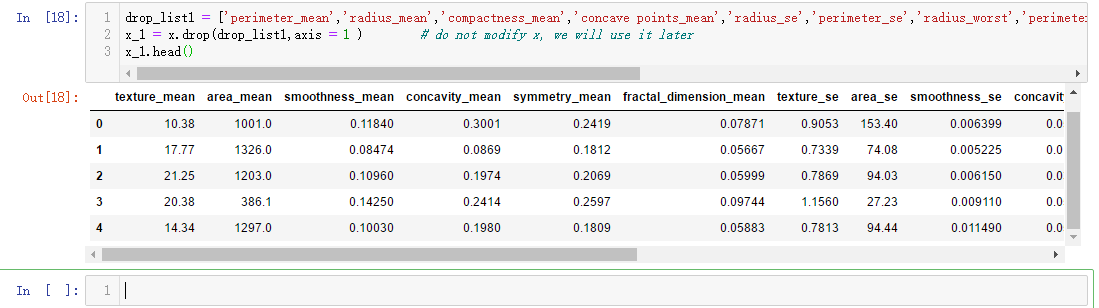
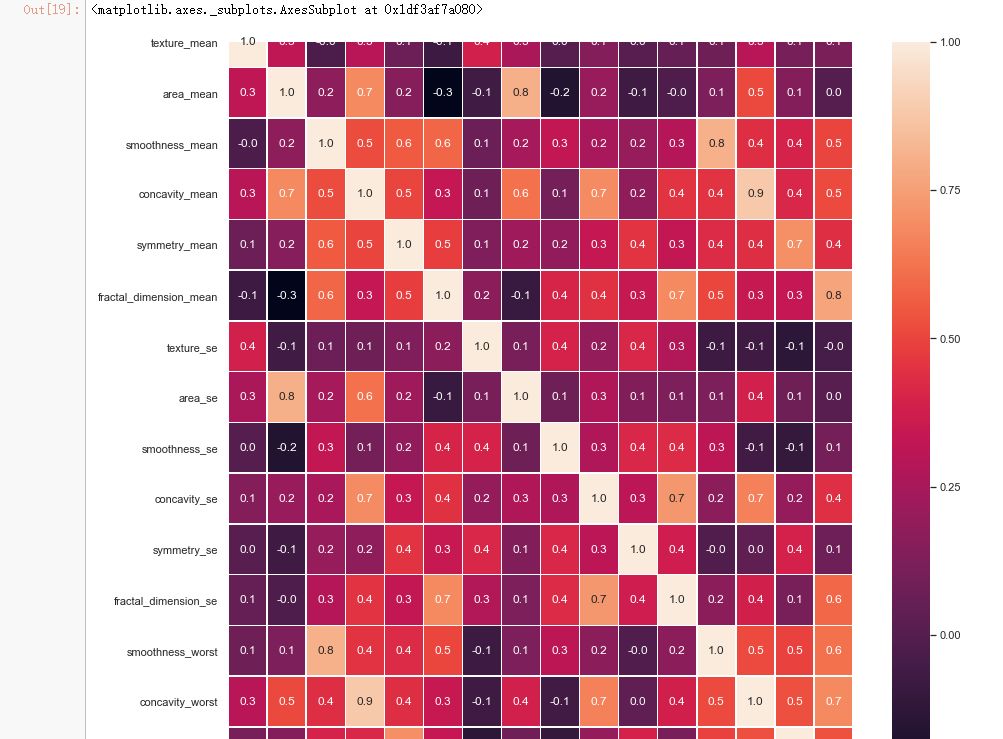
#correlation map
f,ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(14, 14))
sns.heatmap(x_1.corr(), annot=True, linewidths=.5, fmt= '.1f',ax=ax)
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import f1_score,confusion_matrix
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score # split data train 70 % and test 30 %
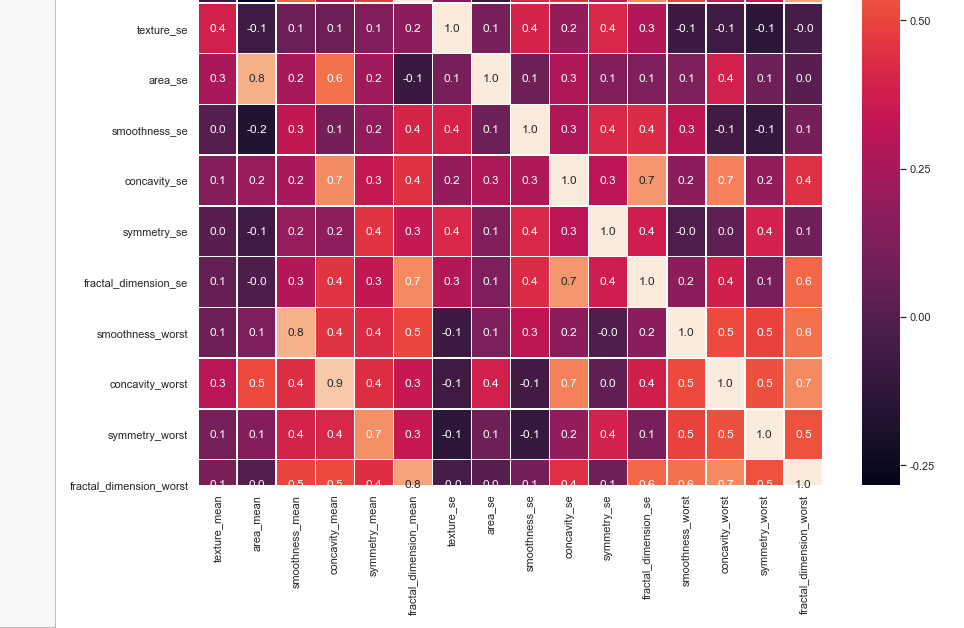
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x_1, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=42) #random forest classifier with n_estimators=10 (default)
clf_rf = RandomForestClassifier(random_state=43)
clr_rf = clf_rf.fit(x_train,y_train) ac = accuracy_score(y_test,clf_rf.predict(x_test))
print('Accuracy is: ',ac)
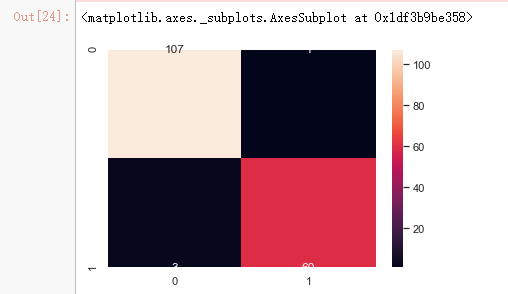
cm = confusion_matrix(y_test,clf_rf.predict(x_test))
sns.heatmap(cm,annot=True,fmt="d")
from sklearn.feature_selection import SelectKBest
from sklearn.feature_selection import chi2
# find best scored 5 features
select_feature = SelectKBest(chi2, k=5).fit(x_train, y_train)
print('Score list:', select_feature.scores_)
print('Feature list:', x_train.columns)

x_train_2 = select_feature.transform(x_train)
x_test_2 = select_feature.transform(x_test)
#random forest classifier with n_estimators=10 (default)
clf_rf_2 = RandomForestClassifier()
clr_rf_2 = clf_rf_2.fit(x_train_2,y_train)
ac_2 = accuracy_score(y_test,clf_rf_2.predict(x_test_2))
print('Accuracy is: ',ac_2)
cm_2 = confusion_matrix(y_test,clf_rf_2.predict(x_test_2))
sns.heatmap(cm_2,annot=True,fmt="d")
from sklearn.feature_selection import RFE
# Create the RFE object and rank each pixel
clf_rf_3 = RandomForestClassifier()
rfe = RFE(estimator=clf_rf_3, n_features_to_select=5, step=1)
rfe = rfe.fit(x_train, y_train)
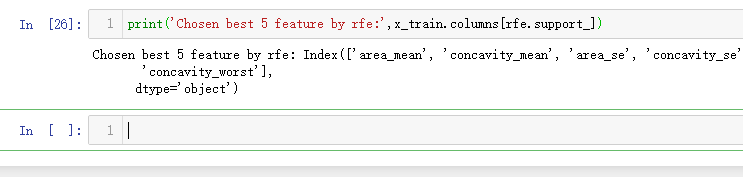
print('Chosen best 5 feature by rfe:',x_train.columns[rfe.support_])
from sklearn.feature_selection import RFECV # The "accuracy" scoring is proportional to the number of correct classifications
clf_rf_4 = RandomForestClassifier()
rfecv = RFECV(estimator=clf_rf_4, step=1, cv=5,scoring='accuracy') #5-fold cross-validation
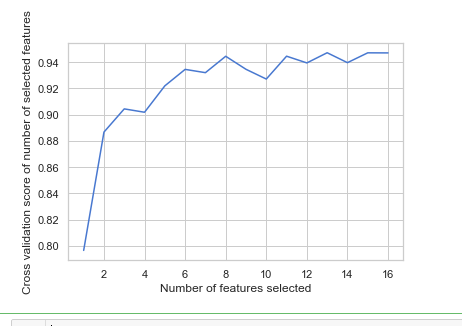
rfecv = rfecv.fit(x_train, y_train) print('Optimal number of features :', rfecv.n_features_)
print('Best features :', x_train.columns[rfecv.support_])
# Plot number of features VS. cross-validation scores
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.figure()
plt.xlabel("Number of features selected")
plt.ylabel("Cross validation score of number of selected features")
plt.plot(range(1, len(rfecv.grid_scores_) + 1), rfecv.grid_scores_)
plt.show()
clf_rf_5 = RandomForestClassifier()
clr_rf_5 = clf_rf_5.fit(x_train,y_train)
importances = clr_rf_5.feature_importances_
std = np.std([tree.feature_importances_ for tree in clf_rf.estimators_],
axis=0)
indices = np.argsort(importances)[::-1] # Print the feature ranking
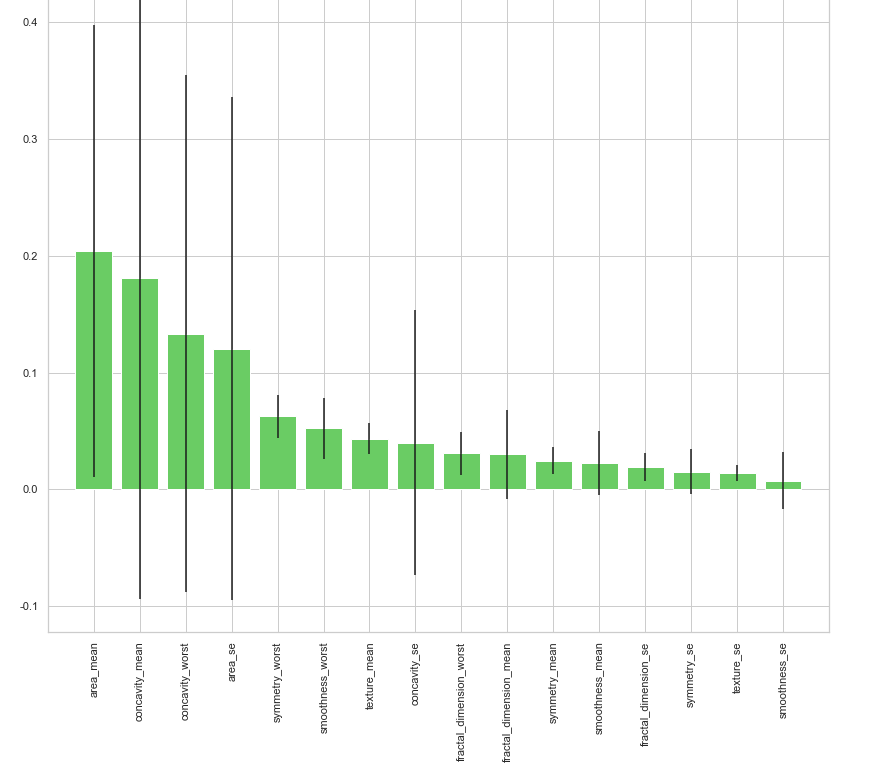
print("Feature ranking:") for f in range(x_train.shape[1]):
print("%d. feature %d (%f)" % (f + 1, indices[f], importances[indices[f]])) # Plot the feature importances of the forest plt.figure(1, figsize=(14, 13))
plt.title("Feature importances")
plt.bar(range(x_train.shape[1]), importances[indices],
color="g", yerr=std[indices], align="center")
plt.xticks(range(x_train.shape[1]), x_train.columns[indices],rotation=90)
plt.xlim([-1, x_train.shape[1]])
plt.show()

# split data train 70 % and test 30 %
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=42)
#normalization
x_train_N = (x_train-x_train.mean())/(x_train.max()-x_train.min())
x_test_N = (x_test-x_test.mean())/(x_test.max()-x_test.min()) from sklearn.decomposition import PCA
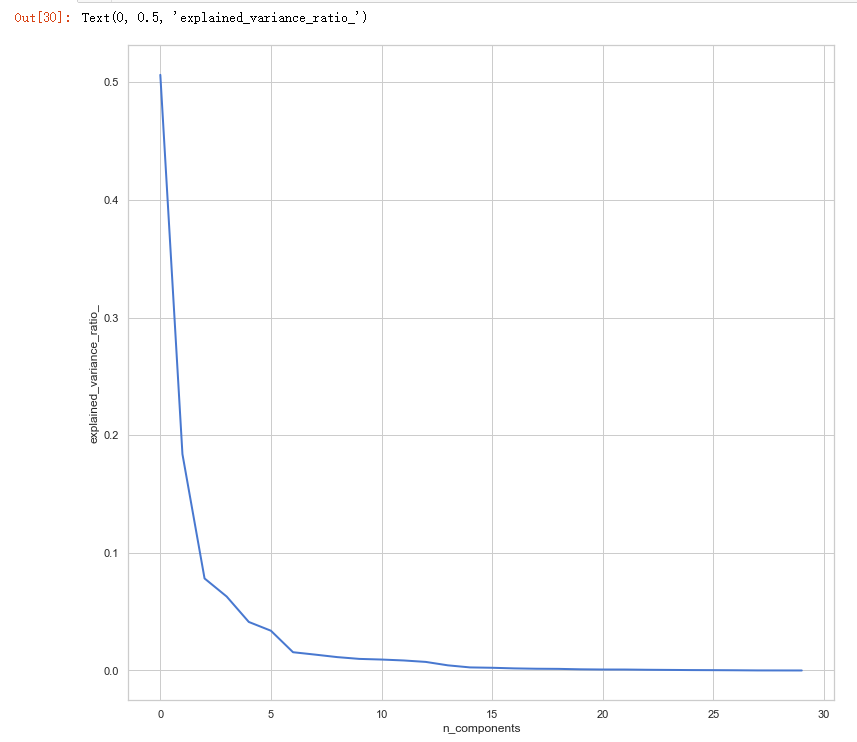
pca = PCA()
pca.fit(x_train_N) plt.figure(1, figsize=(14, 13))
plt.clf()
plt.axes([.2, .2, .7, .7])
plt.plot(pca.explained_variance_ratio_, linewidth=2)
plt.axis('tight')
plt.xlabel('n_components')
plt.ylabel('explained_variance_ratio_')
吴裕雄--天生自然 PYTHON数据分析:威斯康星乳腺癌(诊断)数据分析(续一)的更多相关文章
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 PYTHON数据分析:糖尿病视网膜病变数据分析(完整版)
# This Python 3 environment comes with many helpful analytics libraries installed # It is defined by ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 PYTHON数据分析:所有美国股票和etf的历史日价格和成交量分析
# This Python 3 environment comes with many helpful analytics libraries installed # It is defined by ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 python数据分析:健康指标聚集分析(健康分析)
# This Python 3 environment comes with many helpful analytics libraries installed # It is defined by ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 python数据分析:葡萄酒分析
# import pandas import pandas as pd # creating a DataFrame pd.DataFrame({'Yes': [50, 31], 'No': [101 ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 PYTHON数据分析:人类发展报告——HDI, GDI,健康,全球人口数据数据分析
import pandas as pd # Data analysis import numpy as np #Data analysis import seaborn as sns # Data v ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 python数据分析:医疗费数据分析
import numpy as np import pandas as pd import os import matplotlib.pyplot as pl import seaborn as sn ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 PYTHON语言数据分析:ESA的火星快车操作数据集分析
import os import numpy as np import pandas as pd from datetime import datetime import matplotlib imp ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 python语言数据分析:开普勒系外行星搜索结果分析
import pandas as pd pd.DataFrame({'Yes': [50, 21], 'No': [131, 2]}) pd.DataFrame({'Bob': ['I liked i ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 PYTHON数据分析:基于Keras的CNN分析太空深处寻找系外行星数据
#We import libraries for linear algebra, graphs, and evaluation of results import numpy as np import ...
随机推荐
- vscode Error: ER_NOT_SUPPORTED_AUTH_MODE: Client does not support authentication protocol requested by server; consider upgrading MySQL client
vscode 连接 mysql 时出现这个错误 alter user 'root'@'localhost' identified with mysql_native_password by 'pass ...
- My97DatePicker日历插件
My97DatePicker具有强大的日期功能,能限制日期范围,对于编写双日历比较简便. 注意事项: My97DatePicker目录是一个整体,不可以破坏 My97DatePicker.html 是 ...
- quartz2.2.1bug
quartz2.1.5 调用 scheduler.start()方法时报这样一个异常: 严重: An error occurred while scanning for the next trigge ...
- 计量经济与时间序列_滞后算子和超前算子L的定义
1. 为了使计算简单,引入滞后算子的概念: 2. 定义LYt = Yt-1 , L2Yt = Yt-2,... , LsYt = Yt-s. 3. 也就是把每一期具体滞后哪一期的k提到L的 ...
- win10下挂载efi分区
管理员身份打开cmd 1.输入diskpart, 2.输入list disk,列出所有的disk 3.select disk xxx,xxx代表你要选的disk 数字,比如:select disk 0 ...
- F - No Link, Cut Tree! Gym - 101484F
Marge is already preparing for Christmas and bought a beautiful tree, decorated with shiny ornaments ...
- JS中的7种设计模式
第九章Refactoring to OOP Patterns 重构为OOP模式 7种设计模式: 1,模版方法模式(template method) 2,策略模式(strategy) 3,状态模式(st ...
- 跟踪路由(tracert)及ping命令
由于最近学校网络不好,老是有问题,加上最近写了个数据展示系统,要部署到买的域名下,用到了这两个命令 首先,一台服务器,一台工作站,一个笔记本(我的,来测试ip是否通的) 服务器已经部署了三个网站(一个 ...
- SEERC 2018 Inversion
题意: 如果p数组中 下标i<j且pi>pj 那么点i j之间存在一条边 现在已经知道边,然后求p数组 在一张图中,求有多少个点集,使得这个点集里面的任意两点没有边 不在点集里面的点至少有 ...
- PAT甲级——1041 Be Unique
1041 Be Unique Being unique is so important to people on Mars that even their lottery is designed in ...
