《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 8.42

代码:
%% ------------------------------------------------------------------------
%% Output Info about this m-file
fprintf('\n***********************************************************\n');
fprintf(' <DSP using MATLAB> Problem 8.42 \n\n'); banner();
%% ------------------------------------------------------------------------ % Digital Filter Specifications: Elliptic bandstop
wsbs = [0.40*pi 0.48*pi]; % digital stopband freq in rad
wpbs = [0.25*pi 0.75*pi]; % digital passband freq in rad Rp = 1.0 % passband ripple in dB
As = 80 % stopband attenuation in dB Ripple = 10 ^ (-Rp/20) % passband ripple in absolute
Attn = 10 ^ (-As/20) % stopband attenuation in absolute % Calculation of Elliptic filter parameters: [N, wn] = ellipord(wpbs/pi, wsbs/pi, Rp, As); fprintf('\n ********* Elliptic Digital Bandstop Filter Order is = %3.0f \n', 2*N) % Digital Elliptic bandstop Filter Design:
[bbs, abs] = ellip(N, Rp, As, wn, 'stop'); [C, B, A] = dir2cas(bbs, abs) % Calculation of Frequency Response:
[dbbs, magbs, phabs, grdbs, wwbs] = freqz_m(bbs, abs); % ---------------------------------------------------------------
% find Actual Passband Ripple and Min Stopband attenuation
% ---------------------------------------------------------------
delta_w = 2*pi/1000;
Rp_bs = -(min(dbbs(1:1:ceil(wpbs(1)/delta_w+1)))); % Actual Passband Ripple fprintf('\nActual Passband Ripple is %.4f dB.\n', Rp_bs); As_bs = -round(max(dbbs(ceil(wsbs(1)/delta_w)+1:1:ceil(wsbs(2)/delta_w)+1))); % Min Stopband attenuation
fprintf('\nMin Stopband attenuation is %.4f dB.\n\n', As_bs); %% -----------------------------------------------------------------
%% Plot
%% ----------------------------------------------------------------- figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 8.42 Elliptic bs by ellip function')
set(gcf,'Color','white');
M = 1; % Omega max subplot(2,2,1); plot(wwbs/pi, magbs); axis([0, M, 0, 1.2]); grid on;
xlabel('Digital frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('|H|'); title('Magnitude Response');
set(gca, 'XTickMode', 'manual', 'XTick', [0, 0.25, 0.40, 0.48, 0.75, M]);
set(gca, 'YTickMode', 'manual', 'YTick', [0, 0.01, 0.8913, 1]); subplot(2,2,2); plot(wwbs/pi, dbbs); axis([0, M, -120, 2]); grid on;
xlabel('Digital frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Decibels'); title('Magnitude in dB');
set(gca, 'XTickMode', 'manual', 'XTick', [0, 0.25, 0.40, 0.48, 0.75, M]);
set(gca, 'YTickMode', 'manual', 'YTick', [ -80, -40, 0]);
set(gca,'YTickLabelMode','manual','YTickLabel',['80'; '40';' 0']); subplot(2,2,3); plot(wwbs/pi, phabs/pi); axis([0, M, -1.1, 1.1]); grid on;
xlabel('Digital frequency in \pi nuits'); ylabel('radians in \pi units'); title('Phase Response');
set(gca, 'XTickMode', 'manual', 'XTick', [0, 0.25, 0.40, 0.48, 0.75, M]);
set(gca, 'YTickMode', 'manual', 'YTick', [-1:0.5:1]); subplot(2,2,4); plot(wwbs/pi, grdbs); axis([0, M, 0, 50]); grid on;
xlabel('Digital frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Samples'); title('Group Delay');
set(gca, 'XTickMode', 'manual', 'XTick', [0, 0.25, 0.40, 0.48, 0.75, M]);
set(gca, 'YTickMode', 'manual', 'YTick', [0:20:50]); % ------------------------------------------------------------
% PART 2
% ------------------------------------------------------------ % Discrete time signal
Ts = 1; % sample intevals
n1_start = 0; n1_end = 200;
n1 = [n1_start:n1_end]; % [0:200] xn1 = sin(0.44*pi*n1); % digital signal % ----------------------------
% DTFT of xn1
% ----------------------------
M = 500;
[X1, w] = dtft1(xn1, n1, M); %magX1 = abs(X1);
angX1 = angle(X1); realX1 = real(X1); imagX1 = imag(X1);
magX1 = sqrt(realX1.^2 + imagX1.^2); %% --------------------------------------------------------------------
%% START X(w)'s mag ang real imag
%% --------------------------------------------------------------------
figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 8.42 X1 DTFT');
set(gcf,'Color','white');
subplot(2,1,1); plot(w/pi,magX1); grid on; %axis([-1,1,0,1.05]);
title('Magnitude Response');
xlabel('digital frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Magnitude |H|');
set(gca, 'XTickMode', 'manual', 'XTick', [0, 0.2, 0.44, 0.6, 0.8, 1.0, 1.2, 1.4, 1.56, 1.8, 2]); subplot(2,1,2); plot(w/pi, angX1/pi); grid on; %axis([-1,1,-1.05,1.05]);
title('Phase Response');
xlabel('digital frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Radians/\pi'); figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 8.42 X1 DTFT');
set(gcf,'Color','white');
subplot(2,1,1); plot(w/pi, realX1); grid on;
title('Real Part');
xlabel('digital frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Real');
set(gca, 'XTickMode', 'manual', 'XTick', [0, 0.2, 0.44, 0.6, 0.8, 1.0, 1.2, 1.4, 1.56, 1.8, 2]); subplot(2,1,2); plot(w/pi, imagX1); grid on;
title('Imaginary Part');
xlabel('digital frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Imaginary');
%% -------------------------------------------------------------------
%% END X's mag ang real imag
%% ------------------------------------------------------------------- % ------------------------------------------------------------
% PART 3
% ------------------------------------------------------------
yn1 = filter(bbs, abs, xn1);
n2 = n1; % ----------------------------
% DTFT of yn1
% ----------------------------
M = 500;
[Y1, w] = dtft1(yn1, n2, M); %magY1 = abs(Y1);
angY1 = angle(Y1); realY1 = real(Y1); imagY1 = imag(Y1);
magY1 = sqrt(realY1.^2 + imagY1.^2); %% --------------------------------------------------------------------
%% START Y1(w)'s mag ang real imag
%% --------------------------------------------------------------------
figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 8.42 Y1 DTFT');
set(gcf,'Color','white');
subplot(2,1,1); plot(w/pi,magY1); grid on; %axis([-1,1,0,1.05]);
title('Magnitude Response');
xlabel('digital frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Magnitude |H|');
subplot(2,1,2); plot(w/pi, angY1/pi); grid on; %axis([-1,1,-1.05,1.05]);
title('Phase Response');
xlabel('digital frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Radians/\pi'); figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 8.42 Y1 DTFT');
set(gcf,'Color','white');
subplot(2,1,1); plot(w/pi, realY1); grid on;
title('Real Part');
xlabel('digital frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Real');
subplot(2,1,2); plot(w/pi, imagY1); grid on;
title('Imaginary Part');
xlabel('digital frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Imaginary');
%% -------------------------------------------------------------------
%% END Y1's mag ang real imag
%% ------------------------------------------------------------------- figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 8.42 x(n) and y(n)')
set(gcf,'Color','white');
subplot(2,1,1); stem(n1, xn1);
xlabel('n'); ylabel('x(n)');
title('xn sequence'); grid on;
subplot(2,1,2); stem(n1, yn1);
xlabel('n'); ylabel('y(n)');
title('yn sequence'); grid on;
运行结果:
我自己假设通带1dB,阻带衰减80dB。
在此基础上设计指标,绝对单位,
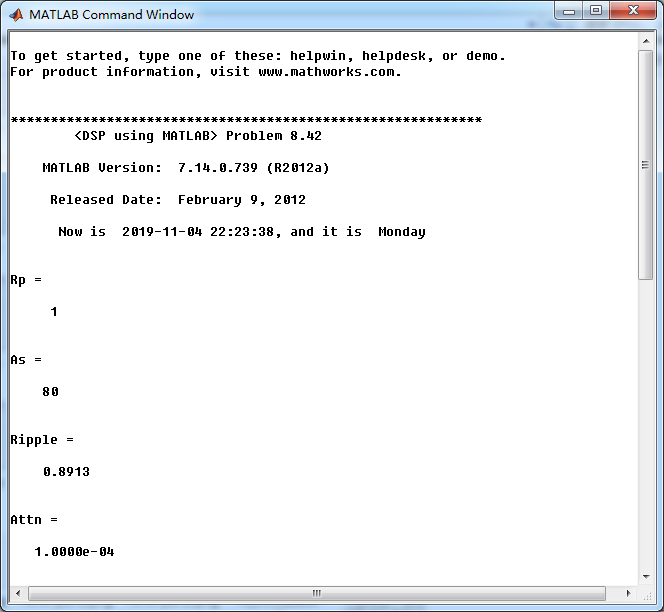
ellip函数(MATLAB工具箱函数)得到Elliptic带阻滤波器,阶数为10,系统函数串联形式系数如下图。
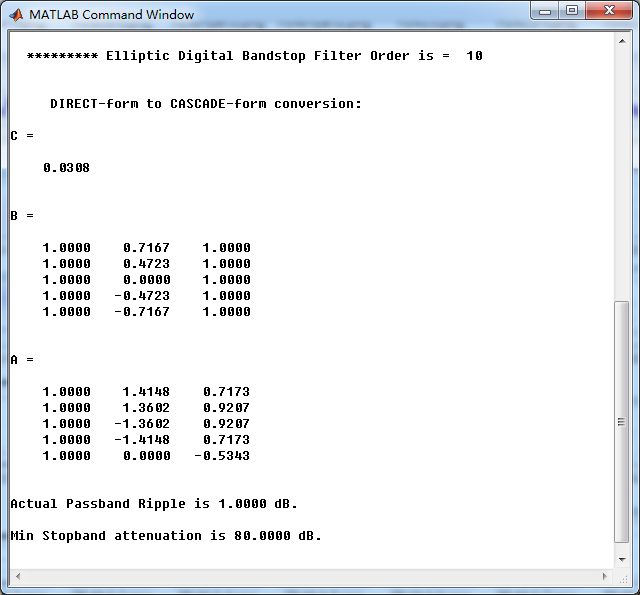
Elliptic带阻滤波器,幅度谱、相位谱和群延迟响应
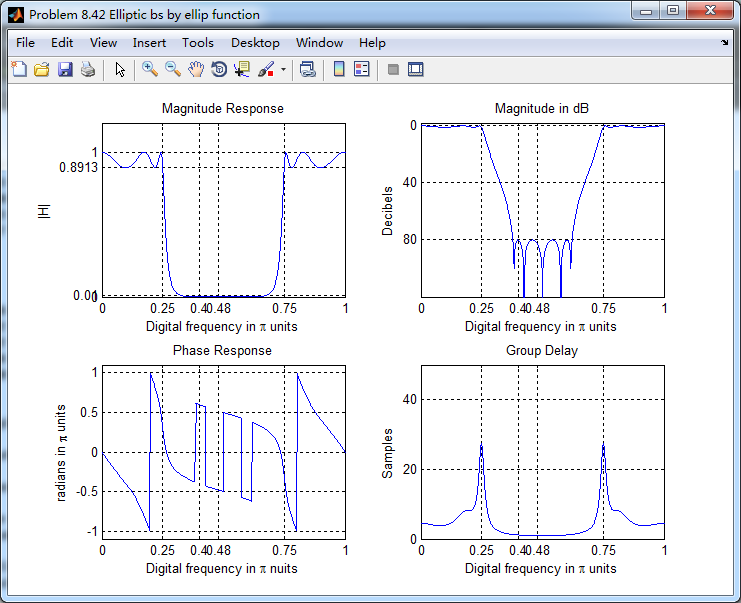
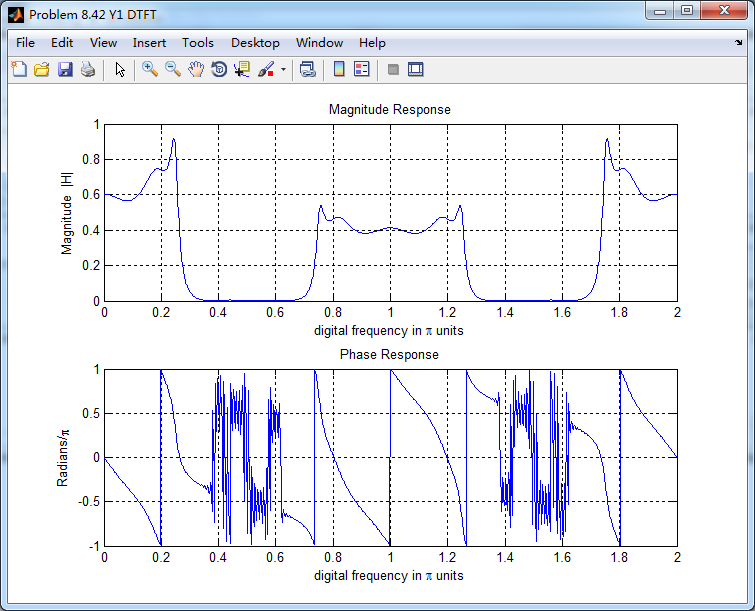
输入离散时间信号x(n)的谱如下,可看出,频率分量0.44π
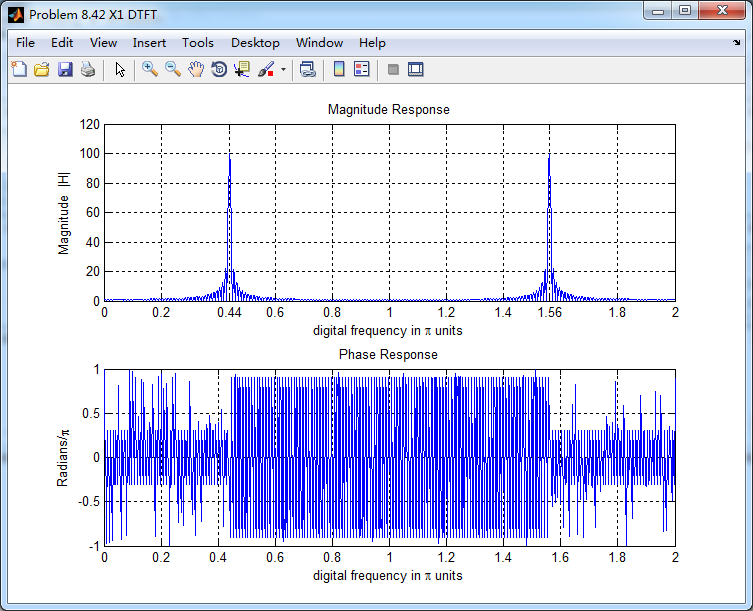
通过带阻滤波器后,得到的输出y(n)的谱,好像变乱了,o(╥﹏╥)o
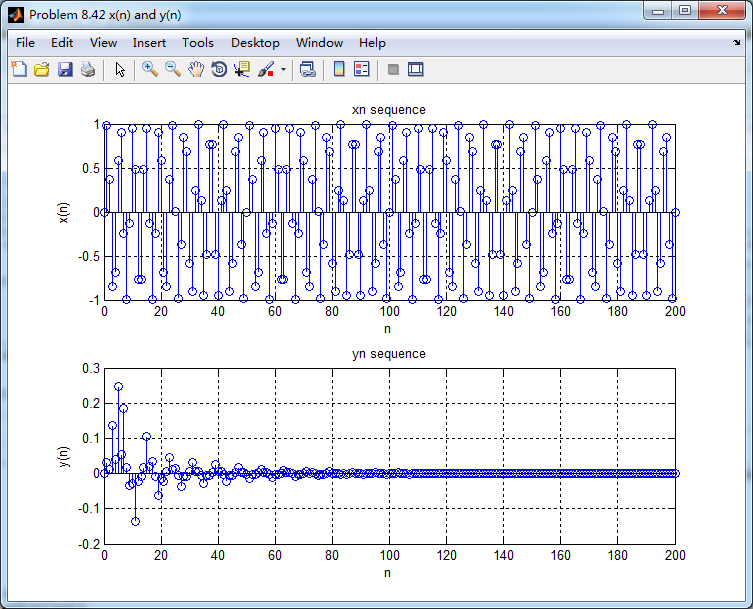
输入和输出的离散时间序列如下图
《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 8.42的更多相关文章
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.14
代码: %% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ %% Output In ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.27
代码: %% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ %% Output In ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.26
注意:高通的线性相位FIR滤波器,不能是第2类,所以其长度必须为奇数.这里取M=31,过渡带里采样值抄书上的. 代码: %% +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.25
代码: %% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ %% Output In ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.24
又到清明时节,…… 注意:带阻滤波器不能用第2类线性相位滤波器实现,我们采用第1类,长度为基数,选M=61 代码: %% +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.23
%% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ %% Output Info a ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.16
使用一种固定窗函数法设计带通滤波器. 代码: %% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.15
用Kaiser窗方法设计一个台阶状滤波器. 代码: %% +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.13
代码: %% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ %% Output In ...
随机推荐
- Android Runnable 运行在那个线程
Runnable 并不一定是新开一个线程,比如下面的调用方法就是运行在UI主线程中的: Handler mHandler=new Handler(); mHandler.post(new Runnab ...
- 用 Windows Live Writer 和 SyntaxHighlighter 插件写高亮代码
博客园内置支持SyntaxHighlighter代码着色,代码着色语法:<pre class='brush:编程语言'>代码</pre>. 需要注意的是:如何你使用Syntax ...
- wmic命令用法小例
wmic就是wmic.exe,位于windows目录底下,是一个命令行程序.WMIC可以以两种模式执行:交互模式(Interactive mode)和非交互模式(Non-Interactive mod ...
- 静态栈-------C语言
/***************************************************** Author:Simon_Kly Version:0.1 Date: 20170520 D ...
- SonarQube搭建和使用教程
我想使用 SonarQube 查阅代码 请问怎么做,现在只有一个要审查代码的项目
- 洛谷 P4173 残缺的字符串 (FFT)
题目链接:P4173 残缺的字符串 题意 给定长度为 \(m\) 的模式串和长度为 \(n\) 的目标串,两个串都带有通配符,求所有匹配的位置. 思路 FFT 带有通配符的字符串匹配问题. 设模式串为 ...
- Codeforces 1191A Tokitsukaze and Enhancement
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/1191/A 思路:枚举 16 种情况输出最高的就行. AC代码: #include<bits/std ...
- 剑指offer——74求1+2+3+n
题目描述 求1+2+3+...+n,要求不能使用乘除法.for.while.if.else.switch.case等关键字及条件判断语句(A?B:C). 题解: 利用类的构造和析构 //利用类的构 ...
- Bootstrap入门及其常用内置实现
BootStrap是一个专门做页面的 1.BS是基于HTML CSS JS 的一个前端框架(半成品) 2.预定义了一套CSS样式与JQurey实现 3.BS和Validation类似,都是JQ的插件, ...
- Django 框架之前
返回主目录:Django框架 内容目录: 一.Django框架之前的内容 1.1 web应用程序的架构 1.2 HTTP协议 1.3 纯手写简单web框架 一.Django框架之前d的内容 1.1 w ...
