吴裕雄--天生自然 PYTHON数据分析:所有美国股票和etf的历史日价格和成交量分析
# This Python 3 environment comes with many helpful analytics libraries installed
# It is defined by the kaggle/python docker image: https://github.com/kaggle/docker-python
# For example, here's several helpful packages to load in import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import statsmodels.tsa.seasonal as smt
import numpy as np # linear algebra
import pandas as pd # data processing, CSV file I/O (e.g. pd.read_csv)
import random
import datetime as dt
from sklearn import linear_model
from sklearn.metrics import mean_absolute_error
import plotly # import the relevant Keras modules
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import Activation, Dense
from keras.layers import LSTM
from keras.layers import Dropout # Input data files are available in the "../input/" directory.
# For example, running this (by clicking run or pressing Shift+Enter) will list the files in the input directory from subprocess import check_output
import os
os.chdir('F:\\kaggleDataSet\\price-volume\\Stocks')
#read data
# kernels let us navigate through the zipfile as if it were a directory # trying to read a file of size zero will throw an error, so skip them
# filenames = [x for x in os.listdir() if x.endswith('.txt') and os.path.getsize(x) > 0]
# filenames = random.sample(filenames,1)
filenames = ['prk.us.txt', 'bgr.us.txt', 'jci.us.txt', 'aa.us.txt', 'fr.us.txt', 'star.us.txt', 'sons.us.txt', 'ipl_d.us.txt', 'sna.us.txt', 'utg.us.txt']
filenames = [filenames[1]]
print(filenames)
data = []
for filename in filenames:
df = pd.read_csv(filename, sep=',')
label, _, _ = filename.split(sep='.')
df['Label'] = filename
df['Date'] = pd.to_datetime(df['Date'])
data.append(df)

traces = []
for df in data:
clr = str(r()) + str(r()) + str(r())
df = df.sort_values('Date')
label = df['Label'].iloc[0]
trace = plotly.graph_objs.Scattergl(x=df['Date'],y=df['Close'])
traces.append(trace) layout = plotly.graph_objs.Layout(title='Plot',)
fig = plotly.graph_objs.Figure(data=traces, layout=layout)
plotly.offline.init_notebook_mode(connected=True)
plotly.offline.iplot(fig, filename='dataplot')

df = data[0]
window_len = 10 #Create a data point (i.e. a date) which splits the training and testing set
split_date = list(data[0]["Date"][-(2*window_len+1):])[0] #Split the training and test set
training_set, test_set = df[df['Date'] < split_date], df[df['Date'] >= split_date]
training_set = training_set.drop(['Date','Label', 'OpenInt'], 1)
test_set = test_set.drop(['Date','Label','OpenInt'], 1) #Create windows for training
LSTM_training_inputs = []
for i in range(len(training_set)-window_len):
temp_set = training_set[i:(i+window_len)].copy() for col in list(temp_set):
temp_set[col] = temp_set[col]/temp_set[col].iloc[0] - 1
LSTM_training_inputs.append(temp_set)
LSTM_training_outputs = (training_set['Close'][window_len:].values/training_set['Close'][:-window_len].values)-1 LSTM_training_inputs = [np.array(LSTM_training_input) for LSTM_training_input in LSTM_training_inputs]
LSTM_training_inputs = np.array(LSTM_training_inputs) #Create windows for testing
LSTM_test_inputs = []
for i in range(len(test_set)-window_len):
temp_set = test_set[i:(i+window_len)].copy() for col in list(temp_set):
temp_set[col] = temp_set[col]/temp_set[col].iloc[0] - 1
LSTM_test_inputs.append(temp_set)
LSTM_test_outputs = (test_set['Close'][window_len:].values/test_set['Close'][:-window_len].values)-1 LSTM_test_inputs = [np.array(LSTM_test_inputs) for LSTM_test_inputs in LSTM_test_inputs]
LSTM_test_inputs = np.array(LSTM_test_inputs)
def build_model(inputs, output_size, neurons, activ_func="linear",dropout=0.10, loss="mae", optimizer="adam"):
model = Sequential()
model.add(LSTM(neurons, input_shape=(inputs.shape[1], inputs.shape[2])))
model.add(Dropout(dropout))
model.add(Dense(units=output_size))
model.add(Activation(activ_func))
model.compile(loss=loss, optimizer=optimizer)
return model
# initialise model architecture
nn_model = build_model(LSTM_training_inputs, output_size=1, neurons = 32)
# model output is next price normalised to 10th previous closing price
# train model on data
# note: eth_history contains information on the training error per epoch
nn_history = nn_model.fit(LSTM_training_inputs, LSTM_training_outputs, epochs=5, batch_size=1, verbose=2, shuffle=True)

plt.plot(LSTM_test_outputs, label = "actual")
plt.plot(nn_model.predict(LSTM_test_inputs), label = "predicted")
plt.legend()
plt.show()
MAE = mean_absolute_error(LSTM_test_outputs, nn_model.predict(LSTM_test_inputs))
print('The Mean Absolute Error is: {}'.format(MAE))

#https://github.com/llSourcell/How-to-Predict-Stock-Prices-Easily-Demo/blob/master/lstm.py
def predict_sequence_full(model, data, window_size):
#Shift the window by 1 new prediction each time, re-run predictions on new window
curr_frame = data[0]
predicted = []
for i in range(len(data)):
predicted.append(model.predict(curr_frame[np.newaxis,:,:])[0,0])
curr_frame = curr_frame[1:]
curr_frame = np.insert(curr_frame, [window_size-1], predicted[-1], axis=0)
return predicted predictions = predict_sequence_full(nn_model, LSTM_test_inputs, 10) plt.plot(LSTM_test_outputs, label="actual")
plt.plot(predictions, label="predicted")
plt.legend()
plt.show()
MAE = mean_absolute_error(LSTM_test_outputs, predictions)
print('The Mean Absolute Error is: {}'.format(MAE))
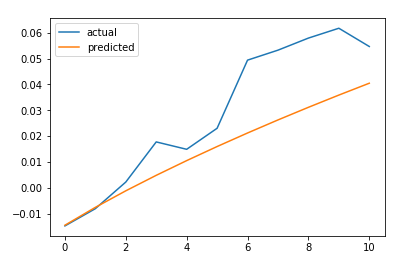
结论
LSTM不能解决时间序列预测问题。对一个时间步长的预测并不比滞后模型好多少。如果我们增加预测的时间步长,性能下降的速度就不会像其他更传统的方法那么快。然而,在这种情况下,我们的误差增加了大约4.5倍。它随着我们试图预测的时间步长呈超线性增长。
吴裕雄--天生自然 PYTHON数据分析:所有美国股票和etf的历史日价格和成交量分析的更多相关文章
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 PYTHON数据分析:糖尿病视网膜病变数据分析(完整版)
# This Python 3 environment comes with many helpful analytics libraries installed # It is defined by ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 python数据分析:健康指标聚集分析(健康分析)
# This Python 3 environment comes with many helpful analytics libraries installed # It is defined by ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 python数据分析:葡萄酒分析
# import pandas import pandas as pd # creating a DataFrame pd.DataFrame({'Yes': [50, 31], 'No': [101 ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 PYTHON数据分析:人类发展报告——HDI, GDI,健康,全球人口数据数据分析
import pandas as pd # Data analysis import numpy as np #Data analysis import seaborn as sns # Data v ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 python数据分析:医疗费数据分析
import numpy as np import pandas as pd import os import matplotlib.pyplot as pl import seaborn as sn ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 PYTHON数据分析:基于Keras的CNN分析太空深处寻找系外行星数据
#We import libraries for linear algebra, graphs, and evaluation of results import numpy as np import ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 python数据分析:基于Keras使用CNN神经网络处理手写数据集
import pandas as pd import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import matplotlib.image as mp ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 PYTHON数据分析:钦奈水资源管理分析
df = pd.read_csv("F:\\kaggleDataSet\\chennai-water\\chennai_reservoir_levels.csv") df[&quo ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 PYTHON数据分析:医疗数据分析
import numpy as np # linear algebra import pandas as pd # data processing, CSV file I/O (e.g. pd.rea ...
随机推荐
- HDU_3415_单调队列
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=3415 初探单调队列,需要注意的是每次i维护的是i-1. #include<iostream> #in ...
- 51Nod 1279 扔盘子 (思维+模拟)
题意: 有口井,往里扔盘子,最多扔多少个 n<=5e5, 1s 思路: 如果比较高的地方井口比较小,那么下面的再大也没有用,只需要维护一个单调减的数组然后O(n+m)模拟即可 代码: #incl ...
- learn about sqlserver partitition and partition table --- add or remove table partitions
demo/* add partitions */ alter database xxx add filegroup FG_=fff_201708;alter database xxx add file ...
- Go语言实现:【剑指offer】题目汇总
所列题目与牛客网<剑指offer>专题相对应. 数组: 和为S的两个数字 和为S的连续正数序列 连续子数组的最大和 数字在排序数组中出现的次数 数组中只出现一次的数字 旋转数组的最小数字 ...
- redis命令总结与持久化
上篇redis文章为大家介绍了redis与它的部署工作.这次我们来说一下redis的操作命令与持久化 一.命令总结 1)String操作 6379> set k1 v1 #设定值 6379> ...
- zabbix的mysql优化后的配置文件
zabbix的mysql数据库导致磁盘IO一直90%以上,访问卡的一逼 改了配置文件最后好了 [root@root /]# cat /etc/my.cnf [mysqld] datadir=/Data ...
- postfix 被当作垃圾邮件中转站
磁盘 io 总是满的状态 该服务器只有监控和邮件elk在上面. 发现邮件日志 疯狂的输出 tail -f /var/log/maillog 大致都是来自于 yahoo.com.tw的东西 清空了 /v ...
- 【转载】STM32 ST-LINK Utility介绍、下载、安装、使用方法
转载地址:https://blog.csdn.net/ybhuangfugui/article/details/52597133 总结的很好!!! Ⅰ.写在前面本文讲述的内容是STM32 ST-LIN ...
- 计算机网络 From Mr.Liu
引言 本博客摘自Mr.Liu,原帖请点击这里. 感谢Mr.Liu,这个文章很充分的描述了计算机网络的核心知识点. 我还在学习中,所以没有进行自己的转述.图片因为是copy代码而没有获得,想看更详尽的, ...
- 解决掉你心中 js function与Function的关系的疑问
前言 在网上有很多关于js function 与 Function直接关系的文章. 但是我感觉过于抽象化了,那么如何是具体化的解释? 正文部分为个人理解部分,如有不对望指出. 正文 <scrip ...
