《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 3.2

1、用x1序列的DTFT来表示x2序列的DTFT

2、代码:
%% ------------------------------------------------------------------------
%% Output Info about this m-file
fprintf('\n***********************************************************\n');
fprintf(' <DSP using MATLAB> Problem 3.2 \n\n'); banner();
%% ------------------------------------------------------------------------ % ----------------------------------
% x1(n)
% ----------------------------------
n1_start = 0; n1_end = 3;
n1 = [n1_start : n1_end]; x1 = [1, 2, 2, 1]; figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 3.2 x1(n)');
set(gcf,'Color','white');
stem(n1, x1);
xlabel('n'); ylabel('x1');
title('x1(n) sequence'); grid on; M = 500;
k = [-M:M]; % [-pi, pi]
%k = [0:M]; % [0, pi]
w = (pi/M) * k; [X1] = dtft(x1, n1, w); magX1 = abs(X1); angX1 = angle(X1); realX1 = real(X1); imagX1 = imag(X1); figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 3.2 DTFT of x1(n)');;
set(gcf,'Color','white');
subplot(2,1,1); plot(w/pi, magX1); grid on;
title('Magnitude Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Magnitude');
subplot(2,1,2); plot(w/pi, angX1); grid on;
title('Angle Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Radians'); X1_chk = (1+exp(-j*w*4)) .* X1;
magX1_chk = abs(X1_chk); angX1_chk = angle(X1_chk); realX1_chk = real(X1_chk); imagX1_chk = imag(X1_chk); figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 3.2 X2(w) obtained by formular with X1(w)');;
set(gcf,'Color','white');
subplot(2,1,1); plot(w/pi, magX1_chk); grid on;
title('Magnitude Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Magnitude');
subplot(2,1,2); plot(w/pi, angX1_chk); grid on;
title('Angle Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Radians'); % -------------------------------------
% x2(n)
% -------------------------------------
[x2, n2] = sigshift(x1, n1, 4); figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 3.2 x2(n)');
set(gcf,'Color','white');
stem(n2, x2);
xlabel('n'); ylabel('x2');
title('x2(n) sequence'); grid on; M = 500;
k = [-M:M]; % [-pi, pi]
%k = [0:M]; % [0, pi]
w = (pi/M) * k; [X2] = dtft(x2, n2, w); magX2 = abs(X2); angX2 = angle(X2); realX2 = real(X2); imagX2 = imag(X2); figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 3.2 DTFT of x2(n)');;
set(gcf,'Color','white');
subplot(2,1,1); plot(w/pi, magX2); grid on;
title('Magnitude Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Magnitude');
subplot(2,1,2); plot(w/pi, angX2); grid on;
title('Angle Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Radians'); % -------------------------------------
% x3(n)
% -------------------------------------
[x3, n3] = sigadd(x1, n1, x2, n2); figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 3.2 x3(n)');
set(gcf,'Color','white');
stem(n3, x3);
xlabel('n'); ylabel('x3');
title('x3(n) sequence'); grid on; M = 500;
k = [-M:M]; % [-pi, pi]
%k = [0:M]; % [0, pi]
w = (pi/M) * k; [X3] = dtft(x3, n3, w); magX3 = abs(X3); angX3 = angle(X3); realX3 = real(X3); imagX3 = imag(X3); figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 3.2 DTFT of x3(n)');;
set(gcf,'Color','white');
subplot(2,1,1); plot(w/pi, magX3); grid on;
title('Magnitude Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Magnitude');
subplot(2,1,2); plot(w/pi, angX3); grid on;
title('Angle Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Radians');
运行结果:
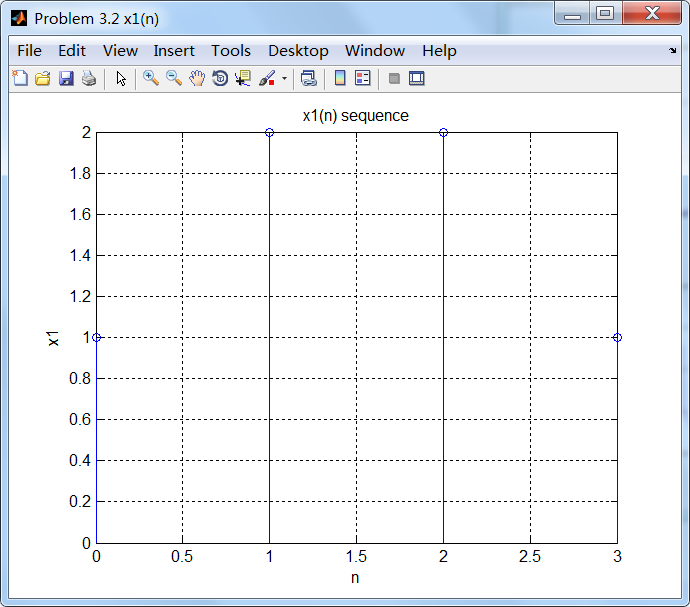

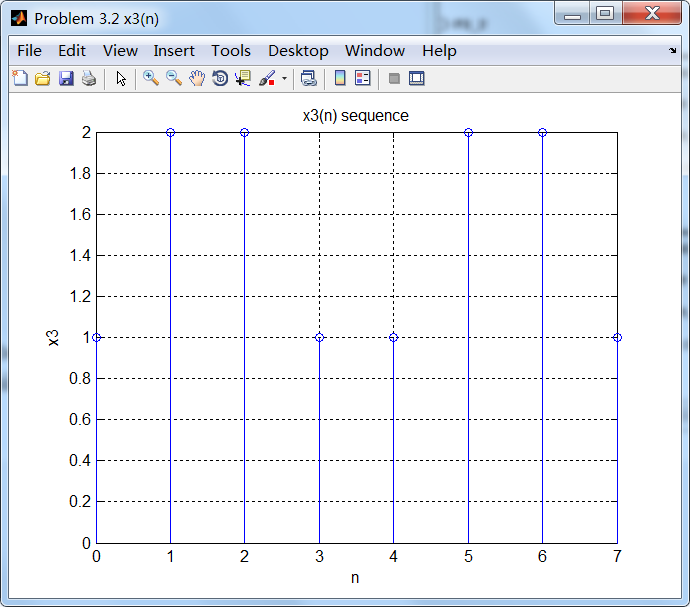

通过第1小题得到的公式计算x2序列的谱,如下:

可看出,第1小题公式计算的结果,和直接将序列通过DTFT定义得到结果是相同的。
《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 3.2的更多相关文章
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.27
代码: %% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ %% Output In ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.26
注意:高通的线性相位FIR滤波器,不能是第2类,所以其长度必须为奇数.这里取M=31,过渡带里采样值抄书上的. 代码: %% +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.25
代码: %% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ %% Output In ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.24
又到清明时节,…… 注意:带阻滤波器不能用第2类线性相位滤波器实现,我们采用第1类,长度为基数,选M=61 代码: %% +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.23
%% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ %% Output Info a ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.16
使用一种固定窗函数法设计带通滤波器. 代码: %% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.15
用Kaiser窗方法设计一个台阶状滤波器. 代码: %% +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.14
代码: %% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ %% Output In ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.13
代码: %% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ %% Output In ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.12
阻带衰减50dB,我们选Hamming窗 代码: %% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ ...
随机推荐
- Java实现最基本的集中排序
排序是一个很重要的概念,现实生活中,我们需要为很多的东西排序.下面我们就介绍几种简单的排序的方法和最基本的思想. 1.冒泡排序:假设一个数组中有10个数字,从左边开始
- poj1673 EXOCENTER OF A TRIANGLE
地址:http://poj.org/problem?id=1673 题目: EXOCENTER OF A TRIANGLE Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 100 ...
- 382. Linked List Random Node(蓄水池采样)
1. 问题 给定一个单链表,随机返回一个结点,要求每个结点被选中的概率相等. 2. 思路 在一个给定长度的数组中等概率抽取一个数,可以简单用随机函数random.randint(0, n-1)得到索引 ...
- ehcache实现页面整体缓存和页面局部缓存
之前写过spring cache和ehcache的基本介绍和注解实现缓存管理,今天记录下web项目的页面缓存技术. 页面缓存是否有必要?. 这样说吧,几乎所有的网站的首页都是访问率最高的,而首页上的数 ...
- Python笔记 #07# NumPy 文档地址 & Subsetting 2D Arrays
文档地址:np.array() 1.<class 'numpy.ndarray'> ndarray 表示 n 维度(n D)数组 (= n 行数组). 2.打印 array 结构 —— n ...
- crontab 定时执行脚本出错,但手动执行脚本正常
原因: crontab 没有去读环境变量,需要再脚本中手动引入环境变量,可以用source 也可以用export 写死环境变量. 为了定时监控Linux系统CPU.内存.负载的使用情况,写了个Shel ...
- atcoder ARC092 D - Two Sequences 二分 & 二进制
今天生日捏,嘻嘻~ 题意:给定A B数组长度为n 求所有 (1<=i,j <=n ) a[i]+b[j] 的异或和. n <=200000 ai bi <=228 这题比赛没 ...
- Java,vue.js,jsp for循环的写法
vue.js <li v-for="student in studentList">{{student.name}}</li> jsp el表达式 < ...
- jsp页面中jstl标签详解[转]
JSLT标签库,是日常开发经常使用的,也是众多标签中性能最好的.把常用的内容,放在这里备份一份,随用随查.尽量做到不用查,就可以随手就可以写出来.这算是Java程序员的基本功吧,一定要扎实. JSTL ...
- Android Studio 中删除项目和项目找回------ Project Structure的使用
删除项目 点击File——Project Structure 在Project Structure页面,选中要删除的项目,点击上面的减号图标. 我把两个一起删除了,再次打开时,啥也没有 如果想要把不要 ...
