吴裕雄--天生自然 PYTHON数据分析:基于Keras的CNN分析太空深处寻找系外行星数据
#We import libraries for linear algebra, graphs, and evaluation of results
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.metrics import roc_curve, roc_auc_score
from scipy.ndimage.filters import uniform_filter1d
#Keras is a high level neural networks library, based on either tensorflow or theano
from keras.models import Sequential, Model
from keras.layers import Conv1D, MaxPool1D, Dense, Dropout, Flatten, BatchNormalization, Input, concatenate, Activation
from keras.optimizers import Adam
INPUT_LIB = 'F:\\kaggleDataSet\\kepler-labelled\\'
raw_data = np.loadtxt(INPUT_LIB + 'exoTrain.csv', skiprows=1, delimiter=',')
x_train = raw_data[:, 1:]
y_train = raw_data[:, 0, np.newaxis] - 1.
raw_data = np.loadtxt(INPUT_LIB + 'exoTest.csv', skiprows=1, delimiter=',')
x_test = raw_data[:, 1:]
y_test = raw_data[:, 0, np.newaxis] - 1.
del raw_data
x_train = ((x_train - np.mean(x_train, axis=1).reshape(-1,1))/ np.std(x_train, axis=1).reshape(-1,1))
x_test = ((x_test - np.mean(x_test, axis=1).reshape(-1,1)) / np.std(x_test, axis=1).reshape(-1,1))
x_train = np.stack([x_train, uniform_filter1d(x_train, axis=1, size=200)], axis=2)
x_test = np.stack([x_test, uniform_filter1d(x_test, axis=1, size=200)], axis=2)
model = Sequential()
model.add(Conv1D(filters=8, kernel_size=11, activation='relu', input_shape=x_train.shape[1:]))
model.add(MaxPool1D(strides=4))
model.add(BatchNormalization())
model.add(Conv1D(filters=16, kernel_size=11, activation='relu'))
model.add(MaxPool1D(strides=4))
model.add(BatchNormalization())
model.add(Conv1D(filters=32, kernel_size=11, activation='relu'))
model.add(MaxPool1D(strides=4))
model.add(BatchNormalization())
model.add(Conv1D(filters=64, kernel_size=11, activation='relu'))
model.add(MaxPool1D(strides=4))
model.add(Flatten())
model.add(Dropout(0.5))
model.add(Dense(64, activation='relu'))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
model.add(Dense(64, activation='relu'))
model.add(Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'))
def batch_generator(x_train, y_train, batch_size=32):
"""
Gives equal number of positive and negative samples, and rotates them randomly in time
"""
half_batch = batch_size // 2
x_batch = np.empty((batch_size, x_train.shape[1], x_train.shape[2]), dtype='float32')
y_batch = np.empty((batch_size, y_train.shape[1]), dtype='float32') yes_idx = np.where(y_train[:,0] == 1.)[0]
non_idx = np.where(y_train[:,0] == 0.)[0] while True:
np.random.shuffle(yes_idx)
np.random.shuffle(non_idx) x_batch[:half_batch] = x_train[yes_idx[:half_batch]]
x_batch[half_batch:] = x_train[non_idx[half_batch:batch_size]]
y_batch[:half_batch] = y_train[yes_idx[:half_batch]]
y_batch[half_batch:] = y_train[non_idx[half_batch:batch_size]] for i in range(batch_size):
sz = np.random.randint(x_batch.shape[1])
x_batch[i] = np.roll(x_batch[i], sz, axis = 0) yield x_batch, y_batch
#Start with a slightly lower learning rate, to ensure convergence
model.compile(optimizer=Adam(1e-5), loss = 'binary_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy'])
hist = model.fit_generator(batch_generator(x_train, y_train, 32),
validation_data=(x_test, y_test),
verbose=0, epochs=5,
steps_per_epoch=x_train.shape[1]//32)
#Then speed things up a little
model.compile(optimizer=Adam(4e-5), loss = 'binary_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy'])
hist = model.fit_generator(batch_generator(x_train, y_train, 32),
validation_data=(x_test, y_test),
verbose=2, epochs=40,
steps_per_epoch=x_train.shape[1]//32)

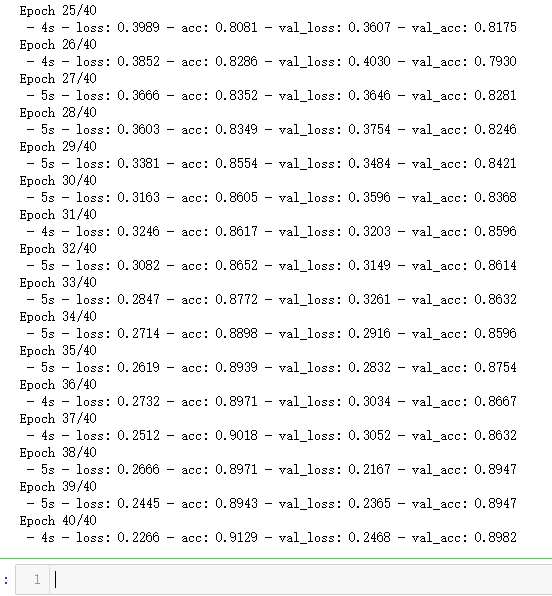
plt.plot(hist.history['loss'], color='b')
plt.plot(hist.history['val_loss'], color='r')
plt.show()
plt.plot(hist.history['acc'], color='b')
plt.plot(hist.history['val_acc'], color='r')
plt.show()
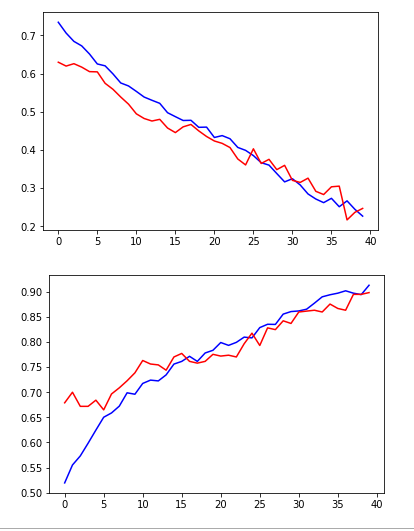
non_idx = np.where(y_test[:,0] == 0.)[0]
yes_idx = np.where(y_test[:,0] == 1.)[0]
y_hat = model.predict(x_test)[:,0]
plt.plot([y_hat[i] for i in yes_idx], 'bo')
plt.show()
plt.plot([y_hat[i] for i in non_idx], 'ro')
plt.show()
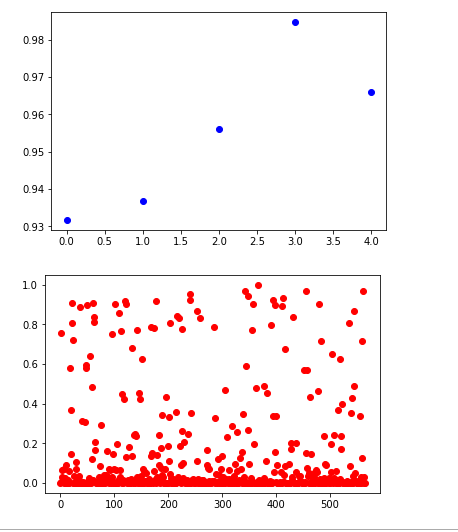
y_true = (y_test[:, 0] + 0.5).astype("int")
fpr, tpr, thresholds = roc_curve(y_true, y_hat)
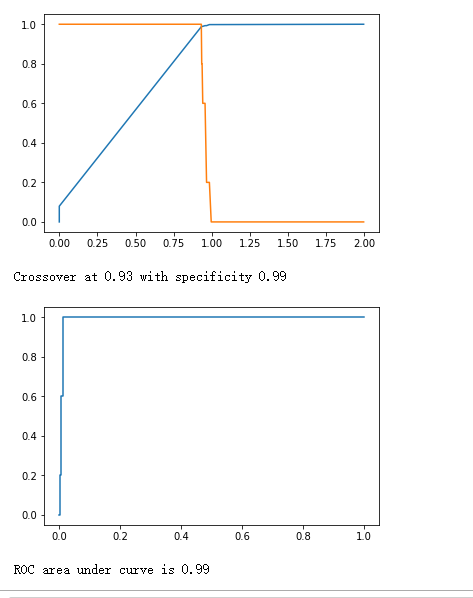
plt.plot(thresholds, 1.-fpr)
plt.plot(thresholds, tpr)
plt.show()
crossover_index = np.min(np.where(1.-fpr <= tpr))
crossover_cutoff = thresholds[crossover_index]
crossover_specificity = 1.-fpr[crossover_index]
print("Crossover at {0:.2f} with specificity {1:.2f}".format(crossover_cutoff, crossover_specificity))
plt.plot(fpr, tpr)
plt.show()
print("ROC area under curve is {0:.2f}".format(roc_auc_score(y_true, y_hat)))
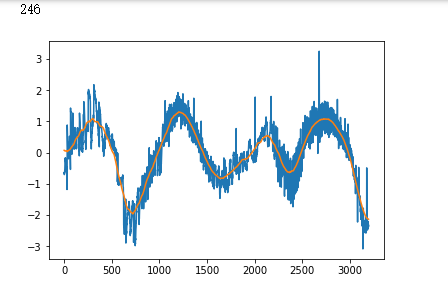
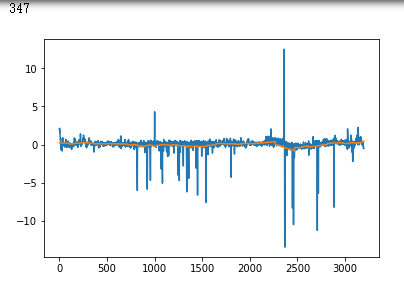
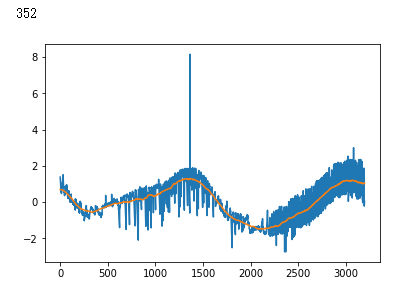
false_positives = np.where(y_hat * (1. - y_test) > 0.5)[0]
for i in non_idx:
if y_hat[i] > crossover_cutoff:
print(i)
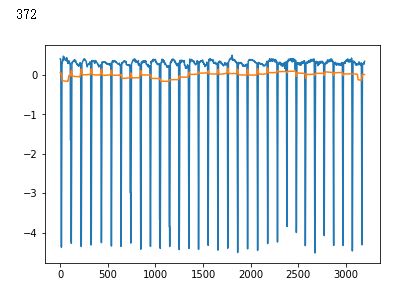
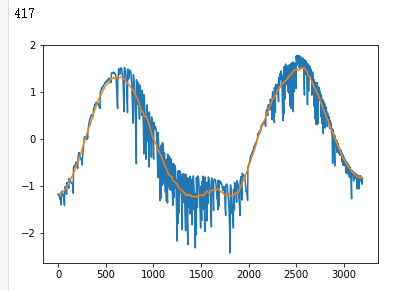
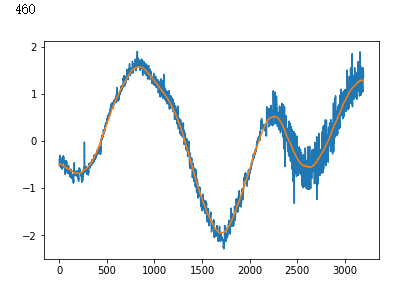
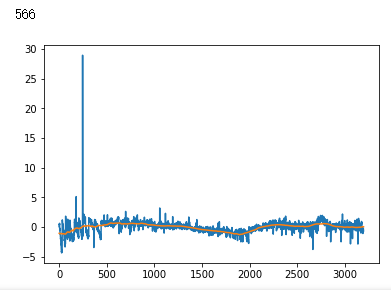
plt.plot(x_test[i])
plt.show()
吴裕雄--天生自然 PYTHON数据分析:基于Keras的CNN分析太空深处寻找系外行星数据的更多相关文章
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 python数据分析:健康指标聚集分析(健康分析)
# This Python 3 environment comes with many helpful analytics libraries installed # It is defined by ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 PYTHON数据分析:钦奈水资源管理分析
df = pd.read_csv("F:\\kaggleDataSet\\chennai-water\\chennai_reservoir_levels.csv") df[&quo ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 python数据分析:基于Keras使用CNN神经网络处理手写数据集
import pandas as pd import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import matplotlib.image as mp ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 PYTHON数据分析:糖尿病视网膜病变数据分析(完整版)
# This Python 3 environment comes with many helpful analytics libraries installed # It is defined by ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 PYTHON数据分析:所有美国股票和etf的历史日价格和成交量分析
# This Python 3 environment comes with many helpful analytics libraries installed # It is defined by ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 python数据分析:葡萄酒分析
# import pandas import pandas as pd # creating a DataFrame pd.DataFrame({'Yes': [50, 31], 'No': [101 ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 PYTHON数据分析:人类发展报告——HDI, GDI,健康,全球人口数据数据分析
import pandas as pd # Data analysis import numpy as np #Data analysis import seaborn as sns # Data v ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 python数据分析:医疗费数据分析
import numpy as np import pandas as pd import os import matplotlib.pyplot as pl import seaborn as sn ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 PYTHON数据分析:医疗数据分析
import numpy as np # linear algebra import pandas as pd # data processing, CSV file I/O (e.g. pd.rea ...
随机推荐
- ZJNU 1333 - 第二题 blocks--中高级
因为放一个就需要判断一次,每一次跑一遍全图bfs显然是不现实的 又因为点只有三种,黑白无 所以可以用并查集优化 添加一个棋子就判断周围四个的组别情况 注意出现的情况与答案关系之间的判别 /* Writ ...
- P2P平台爆雷不断到底是谁的过错?
早在此前,范伟曾经在春晚上留下一句经典台词,"防不胜防啊".而将这句台词用在当下的P2P行业,似乎最合适不过了.就在这个炎热夏季,P2P行业却迎来最冷冽的寒冬. 引发爆雷潮的众多P ...
- protobuf使用遇到的坑
在这里具体的使用我不写了,可以参考下面接个连接,我只记录自己遇到的问题. https://www.cnblogs.com/autyinjing/p/6495103.html(此博客很详细,不过最好不要 ...
- [Algo] 625. Longest subarray contains only 1s
Given an array of integers that contains only 0s and 1s and a positive integer k, you can flip at mo ...
- 对于 C语言的扩展和JAVA的重载理解
哎,又被学长看成笨蛋了 ,先前学习java,自己真是什么都要忘了,弄得自己连java最重要的概念--重载,都不知道是啥,还厚着脸皮和学长说 是函数名字一样 ,但是就是函数里面的参数和参数类型不一 ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 PYTHON3开发学习:正则表达式
import re print(re.match('www', 'www.runoob.com').span()) # 在起始位置匹配 print(re.match('com', 'www.runoo ...
- Gym 101987K TV Show Game(2-SAT)
题目链接:https://vj.z180.cn/b4aacc08fc7aab6ce14e7baf13816c24?v=1571542994 题目要求n个灯(R,B),给出m组赋值方式,每一组中至少有两 ...
- Downton Abbey
1. 当女儿以为泰坦尼克号不会沉的时候,父亲用了一个有意思的比喻: - I thought it was supposed to be unsinkable. - Every mountain is ...
- 功能区按钮调用Excel、PowerPoint、Word中的VBA宏:RunMacro
功能区按钮调用Excel.PowerPoint.Word中的VBA宏:RunMacro 众所周知,Excel.PPT.Word文档或加载宏文件中可以写很多过程和函数,调试的过程中当然可以按F8或F5直 ...
- Linux centos 下安装redis
一.安装编译工具及库文件 yum -y install make zlib zlib-devel gcc-c++ libtool openssl openssl-devel 二.选择安装文件 ...
